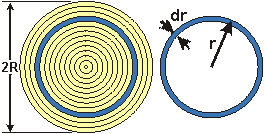
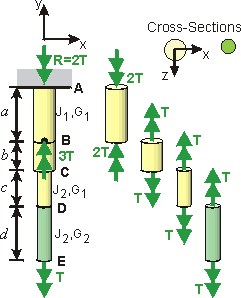
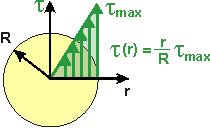If the torque, cross-section and material are all constant over the length, then the following relationships hold for shear strain and shear stress:
![]()
Combining the above equations with Hooke's law:
t = Gg
give the angle of twist:
J is the Polar Moment of Inertia.
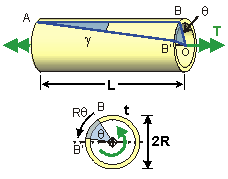
Thin-walled circular shaft