Equilibrium
Once a FBD system is constructed, the next step is to apply the conditions of equilibrium. A
body in static equilibrium is not accelerating, so the forces and moments
acting on it must sum to zero in any direction. Equilibrium requires that:
- the sum of the forces in any direction must be zero: S F = 0.
- the sum of the moments about any non-accelerating point must be zero: S MO= 0.
In 3-dimensions, six equations must be satisfied:
S Fx = 0 ; S Fy = 0 ; S Fz = 0
S Mx = 0 ; S My = 0 ; S Mz = 0 |
In 2-dimensions, only three equilibrium equations are required.
When the object is in the x-y plane, one of the following three
sets of equations may be used:
S Fx = 0
S Fy = 0
S Mz,A = 0
|
S Fx = 0
S Mz,A = 0
S Mz,B = 0
|
S Mz,A = 0
S Mz,B = 0
S Mz,C = 0
|
| The sum of forces in x and in y, and the
sum of moments about any Point A (about a z-axis through Pt. A), each equal zero |
Points A and B are two
different points. |
A, B and C are
three points, not all on the same line. The points define a plane. |
Many 3D-problems can be reduced to 2-D. |
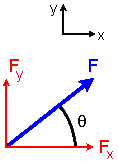 Vectors and Forces
Vectors and Forces